Describe the Difference Between a Typical Galaxy and a Quasar
An astronomer observes the light from a nearby galaxy. A quasar is powered by a supermassive black hole at the centre of a galaxy.

Lecture 27 Quasars And Active Galaxies Agn S
The brighter quasars have a luminosity of 10 15 L Sun 100000 x more luminous than the Milky Way.

. In what ways are active galaxies like quasars but different from normal galaxies. A typical quasar is several times brighter than an entire galaxy that has no quasarQuite a bit more than that. Its spectrum however shows that it is moving away from us at a speed of 36 the speed of light or 67000 miles per second.
A Quasar is an Active Galactic Nuclei it is the centre of a galaxy that is shooting out a stream of particles from the centre. Describe one way astronomers measure the distance to stars. Describe the arguments supporting the idea that quasars are at the distances indicated by their redshifts.
Describe some differences between quasars and normal galaxies. Describe Difference between coaxial cable and twisted pair cable. One of the big differences between AGN and quasars on the one hand and regular old galaxies on the other is luminosity.
Quasars are 10 to 100 times more luminous than brighter normal galaxies. The Milky Way was believed to have been a Quasar once but is currently quiet. Normal galaxies are observed throughout the universe while quasars are.
Gas in the disc falling towards the black hole heats up because of friction and releases energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Our galaxy is about 100000 light years across and about 1000 light years thick. An obvious consequence is that AGN such as quasars will in general be visible at much larger distances than ordinary galaxies.
If material is constantly falling into the accretion disc it gets heated by friction and the gravity of the black hole to the point where it emits vast amounts of energy. Quasars emission lines shifts far to the red wavelength ranging from 15 to more than 96 the speed of light while a normal galaxy have both red and blue shifts. Some of the apparent differences between types of AGN are due to our having different orientations with respect to the disk.
Many galaxies including our own Milky Way. Explain the difference between absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude. AGN emit much more energy at all wavelengths.
Explain how a quasar differs from a typical galaxy. An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy having an. The top left image shows a quasar that lies at the heart of a spiral galaxy 14 billion light-years from Earth.
Describe some differences between quasars and normal galaxies. Note that nothing in this image distinguishes the quasar from an ordinary star. Describe at least four differences between elliptical and spiral galaxies.
Spiral galaxies are named by their spiral structures that extend from the center into the galactic disc. Suppose you do find one and only one galaxy with a quasar very close by and the redshift of the quasar is six times larger than that of the galaxy. Seyfert galaxies are lower-luminosity active galactic nuclei withMB -2151 5 log h0for theactive nucleus the generally accepted criterion due originally to Schmidt Green 1983 fordistinguishing Seyfert galaxies from quasars.
Quite a bit more than that. The Hubble Space Telescope reveals the much fainter host galaxies around quasars. Theoriginal definition of the class Seyfert.
The spectrum of light from an astronomical object called a quasar can be compared to the. Describe some differences between quasars and normal galaxies. Quasars are Active Galactic Nuclei AGN Later more powerful telescopes have shown that the QSOs have faint galaxies surrounding them suggesting that the Quasars are the very bright nuclei of active galaxies.
The difference between a Quasar and a Blazar is how it is angled towards us. Describe Difference between coaxial cable and twisted pair cable. Describe the difference between an typical galaxy and a quasar.
A quasar is an extremely luminous active galactic nucleus powered by a supermassive black hole with mass ranging from millions to tens of billions of solar masses surrounded by a gaseous accretion disc. With blazars and quasars we are looking down the jet. The bottom left image shows a quasar that lies at the center of an elliptical galaxy some 15 billion light-years from us.
A Seyfert galaxy has aquasar-like nucleus but the host galaxy is clearly detectable. The spiral arms are sites of ongoing star formation and are brighter than the surrounding disc because of the young hot OB stars that inhabit them. Describe the arguments supporting the idea that quasars are at the distances indicated by their redshifts.
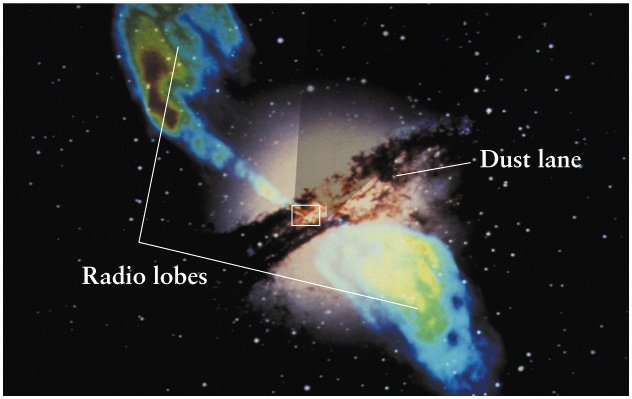
Radio galaxies quasars and blazars are AGN with strong jets that can travel outward into large regions of intergalactic space. -more luminous and compact. The radiant energy of quasars is.
-the redshifts of the underlying galaxies match the redshifts of the quasars in their center. Quasars infrared and X-ray bands are brighter than normal galaxy. Quasar and Blazars are not stars they are a type of galaxy.
Given that our own Milky Way Galaxy is a normal spiral galaxy one can only use these details as a typical galaxy. Describe the three main types of galaxies. Describe the difference between the nucleus of gallium-68 and the nucleus of gallium-67.
The black hole has a disc of material spiralling into it called an accretion disc. Normal galaxies host anywhere from thousands of stars in the smallest galaxies to trillions of stars in the largest ones. The arrow in this image marks the quasar known by its catalog number PKS 1117-248.
Explain how Hubbles discoveries lead to an understanding that the universe is expanding. Quasars appear to be single solitary energy sources. One way was to find a mismatched paira quasar and a galaxy with different redshifts that lie in very nearly the same direction in the sky.
How does Chaucer characterize the participants in The Canterbury Tales.

How Can You Tell The Difference Between A Quasar And An Asteroid Just Ask G10 International School Utrecht International School Utrecht
No comments for "Describe the Difference Between a Typical Galaxy and a Quasar"
Post a Comment